Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) algorithm has brought a significant change in how search engines understand user intent, making it essential for businesses and digital marketers to understand its impact on SEO.
This guide explores how BERT works, its effects on SEO strategies, and practical ways to adapt to these changes in online search.

When Was BERT Introduced to Google Search?
BERT was introduced to Google Search in October 2019, starting with English-language queries, and it has since been expanded to other languages.
Google considers BERT one of the biggest advancements in the history of search because it allows the search engine to better understand the context of user queries, especially longer, conversational ones.
What is BERT?
BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, is a neural network-based technique for natural language processing.
Unlike traditional models that process text sequentially, BERT reads the entire sentence at once, understanding words in the context of those around them. This capability makes it more effective at grasping the meaning of complex queries.
For example, BERT can differentiate between the phrases “to sell” and “to buy,” understanding that “to” has different implications in each context. This nuanced understanding is essential for delivering more relevant search results.
For more technical details about BERT, you can read the original research paper here.
How Does BERT Work?
The key to BERT’s success lies in its bidirectional training, which is a part of Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP allows algorithms to understand and interpret human language more naturally.
Unlike traditional models that process words in a linear order (left to right), BERT analyzes the entire sentence simultaneously, looking at both the words before and after.
This bidirectional approach enables BERT to grasp the full context, leading to a deeper and more accurate understanding of the text.
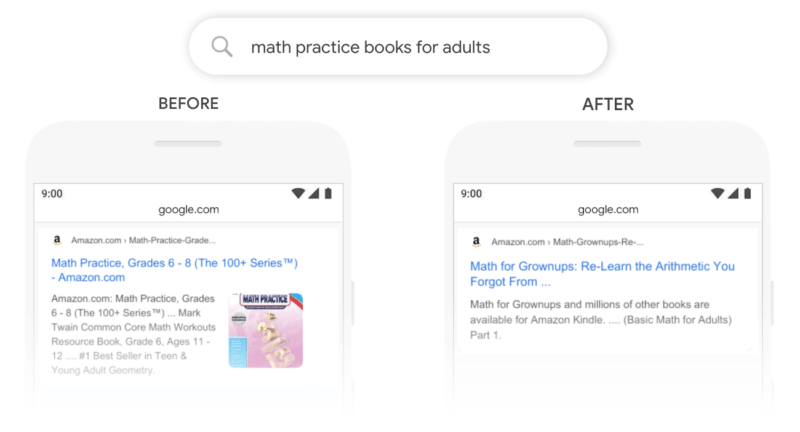
Example: The image below illustrates how BERT improved the search results for the query “math practice books for adults.” Before BERT, the top result was a children’s math book, which didn’t match the user’s intent.
After BERT, the search engine provided a more relevant book specifically for adults, showing how BERT accurately interprets the query’s context.
The Impact of BERT on SEO
BERT has shifted the focus of SEO towards understanding user intent, making it essential for content to address users’ needs directly and naturally.
However, keyword-based optimization remains important. The key is to use keywords thoughtfully, ensuring they fit naturally within the content.
Overusing keywords can lead to a “spammy” feel, which Google may penalize, impacting your search rankings.
Here’s how BERT has impacted SEO practices:
- Focus on Natural Language – Content should prioritize readability and natural phrasing. Write in a way that mirrors how people naturally speak and search, rather than forcing keywords into every sentence.
- Long-Tail Keywords – BERT’s understanding of language makes it easier to rank for long-tail keywords that reflect realistic, conversational queries. These can capture specific search intents and improve your content’s relevance.
- User Intent – BERT focuses on the intent behind queries. Content should be created with a deep understanding of what users are actually looking for, rather than just trying to match keywords
How to Use BERT to Your Advantage in SEO
To leverage BERT effectively in your SEO strategy, focus on creating content that aligns with how Google processes and understands language:
- Prioritize Quality Content – Write content that directly addresses user queries with clear, concise, and informative information. Instead of focusing solely on keywords, aim to solve the user’s problem or answer their question in a natural and engaging way.
- Embrace Conversational Phrasing – Since BERT excels at understanding natural language, incorporating conversational and long-tail phrases can help match user intent. Think about how users might phrase their searches and include those variations in your content.
- Optimize for Featured Snippets – Structure your content to provide clear, direct answers to common questions. BERT helps Google understand complex queries, making it easier for well-structured content to appear in featured snippets. Use headers, lists, and straightforward language to enhance your chances.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing – While keywords are still necessary, they should be used sparingly and naturally. Overstuffing can lead to a negative ranking impact. Focus on relevant, context-driven keywords that naturally fit the content.
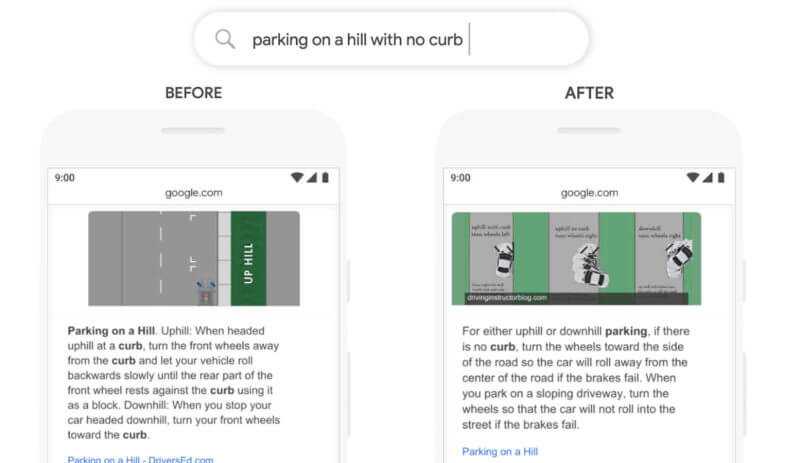
This example shows how BERT helps Google improve featured snippets. By understanding complex queries more accurately, BERT ensures that well-structured content, like the one addressing ‘parking on a hill with no curb,’ appears in snippets, providing clear and relevant answers.
The Future of BERT SEO and AI in Search
BERT has set a new standard in natural language processing, but it is not the end. Future AI advancements will build on BERT’s foundation, improving the search engine’s ability to understand and respond to user queries.
This could lead to even better results for voice search, more personalized responses, and integration with other Google products, like Google Assistant.
FAQs About BERT & SEO
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is an algorithm that helps Google better understand the context of words in search queries, enabling more accurate search results. It focuses on natural language processing (NLP) to interpret user intent.
Yes, Google continues to use BERT to improve the understanding of complex, conversational queries, ensuring more relevant search results.
BERT is used to analyze the context and meaning of words within search queries, helping Google deliver more precise and relevant answers, especially for longer, conversational searches.
Absolutely. BERT remains a core part of Google’s search algorithm, essential for understanding natural language and improving user experience across diverse queries.



